Understanding The Distance Between Objects Decreasing The Masses Of The Objects
The universe is a vast expanse filled with mysteries that often perplex even the most knowledgeable scientists. One intriguing phenomenon is how the distance between objects can influence their masses. This topic is not only fascinating but also vital in the fields of physics and astronomy. As we delve deeper into this subject, it becomes essential to understand the principles of gravity, mass, and the implications of distance in the universe.
When we think about mass, we typically associate it with the amount of matter in an object. However, the gravitational pull that objects exert on each other changes based on the distance separating them. This relationship raises many questions about how we perceive and measure mass in different contexts. Exploring these concepts can lead to a better understanding of gravitational forces and the dynamics of celestial bodies.
Furthermore, the distance between objects decreasing the masses of the objects and can lead us into discussions about the nature of spacetime, the fabric of our universe. How do these distances influence the gravitational interactions that govern everything from the orbits of planets to the behavior of particles? By examining these relationships, we can not only gain insights into physics but also appreciate the intricate balance that sustains the universe.
What is the Relationship Between Distance and Mass?
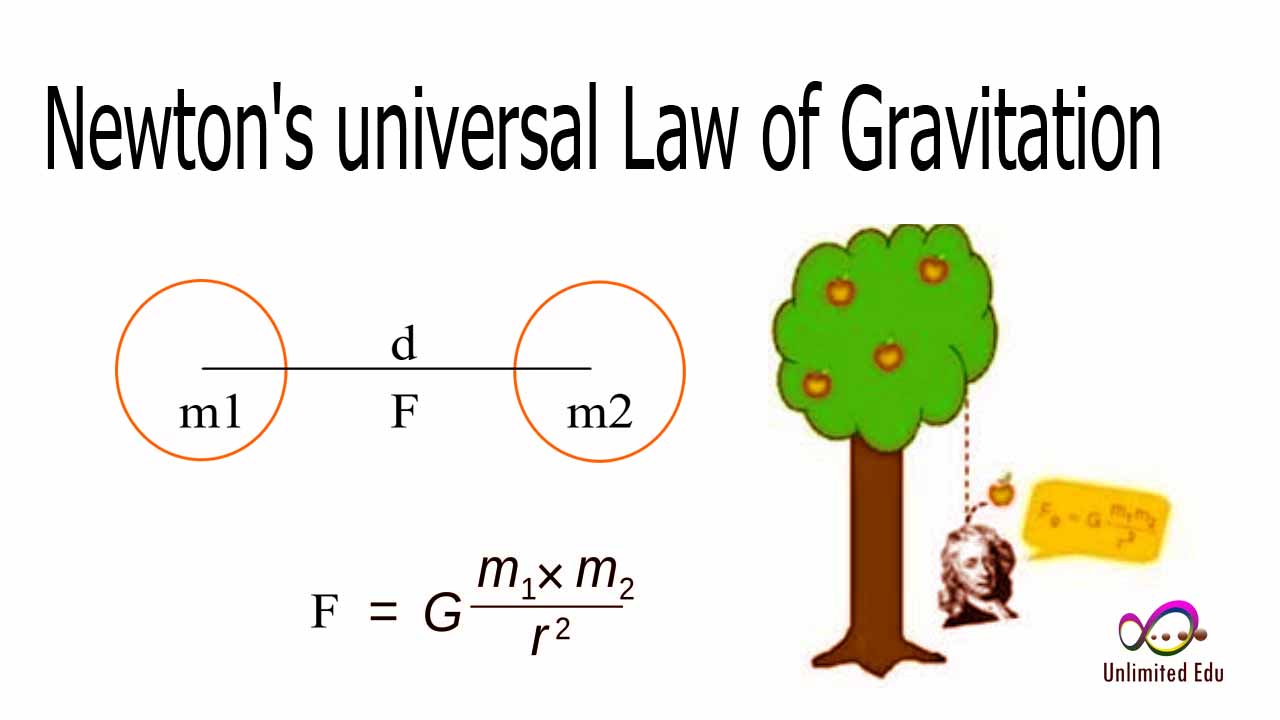
The relationship between distance and mass is primarily governed by Newton's law of universal gravitation, which states that every point mass attracts every other point mass with a force that is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers. This means that as the distance between two objects increases, the gravitational force they exert on each other decreases. This relationship has profound implications for both small-scale interactions and large-scale cosmic dynamics.
How Does Distance Affect Gravitational Force?
As the distance between two objects increases, the gravitational force acting between them diminishes. This can be expressed mathematically through the formula:
F = G * (m1 * m2) / r²
Where:
- F is the gravitational force between the objects.
- G is the gravitational constant.
- m1 and m2 are the masses of the objects.
- r is the distance between the centers of the two masses.
This equation clearly illustrates that as "r" (the distance) increases, the force "F" decreases, highlighting how crucial distance is in understanding gravitational interactions.
Can Mass Change with Distance?
While the gravitational force decreases with distance, it is important to clarify that the intrinsic mass of an object does not change. What changes is the gravitational influence that the object has on others and vice versa. This distinction is vital in discussions concerning relativity and the behavior of objects in different gravitational fields.
How Does This Concept Apply to Celestial Bodies?
The distance between celestial bodies is a critical factor in their interactions. For example, the Earth and the Moon have a specific distance that allows them to maintain their gravitational relationship, influencing tides and orbital dynamics. If the distance were to change significantly, the gravitational effects would also alter, leading to substantial shifts in behavior.
What Are the Practical Implications of Mass and Distance in Space Exploration?
Understanding the relationship between mass and distance is crucial for space missions. For instance, when launching spacecraft, scientists must consider the gravitational pull of Earth, the trajectory needed to escape its gravity, and the distances involved when approaching other celestial bodies. This knowledge informs everything from fuel requirements to navigation strategies.
Does Distance Between Objects Decrease the Masses of the Objects and Their Interaction?
As previously mentioned, while the distance between the objects decreasing the masses of the objects and does not actually change their masses, it does affect their gravitational interactions. This can alter how objects behave in space, such as the orbits of planets, the behavior of galaxies, and the formation of stellar systems. Understanding these dynamics is essential for astrophysics and cosmology.
What Are the Theoretical Considerations of Distance and Mass?
Theoretically, various models in physics explore the intricate relationship between distance and mass. In general relativity, for instance, the curvature of spacetime is influenced by mass and energy. As objects move through curved spacetime, their paths are altered, which can also be understood in terms of distance. The interplay between these concepts leads to a deeper understanding of the universe’s structure and evolution.
How Can We Measure the Distance Between Objects in Space?
Measuring distances in space is a complex but essential task that astronomers undertake using various methods, including:
- Parallax: Observing the apparent shift in position of an object from different vantage points.
- Standard Candles: Using known luminosity of certain stars to estimate distance based on their brightness.
- Redshift: Analyzing the shift in light waves from distant galaxies to determine how far away they are.
These methods help scientists understand not just how far apart objects are, but also how their distances influence their masses and gravitational relationships.
Conclusion: The Interplay of Distance and Mass in Our Universe
The distance between the objects decreasing the masses of the objects and their gravitational interactions is a fundamental principle that shapes our understanding of the universe. From the orbits of planets to the behavior of galaxies, this relationship plays a vital role in the cosmic dance of matter and energy. As we continue to explore the universe, the interplay of distance and mass will remain a cornerstone of our scientific inquiry, helping us unravel the mysteries of the cosmos.
Article Recommendations
- Jordin Sparks
- Who Is Calvin Johnsons Wife
- Jessica Tarlov First Husband
- Simon Cowel
- Perlman Actress
- Streameastis
- Diddy And Justin Bieber
- Liam Payne Fork
- Zin Manga
- Matt Smith Girlfriend